Ultra-High Performance Gyroscope for Future X-ray Interferometer Missions
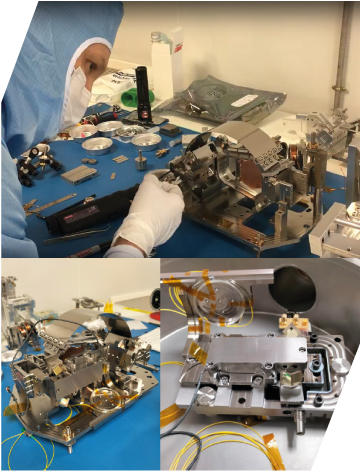
The ODIN project, funded by the European Space Agency (ESA), is led by MAÅGM and brings together a consortium of Europe’s most prestigious experts in gyroscope and pointing technologies, including LMU Munich (Giant-RLG), Elproma (Giant-FOG), LTE Paris (Cold-atom gyro), Sodern (Star tracker), and IPGP (Planetology instruments). Its objective is to evaluate and define a technological roadmap for the development of an ultra-high-performance gyroscope working in conjunction with a star tracker, suited for future space missions. These missions, such as X-ray interferometry envisioned with the future Athena X-ray telescope, aim to achieve microarcsecond angular resolution, requiring pointing accuracy far beyond current AOCS capabilities. ODIN explores the performance, architecture, and technologies necessary to meet these extraordinary requirements and reinforce Europe’s leadership in high-grade space instrumentation.